B2B Data Quality: Is Data Still the New Oil?
Published by Bryce Jones on October 3, 2022
Undergoing successful digital transformations and shifting towards data-driven processes requires businesses data quality to be of high quality, that is accurate and actionable.
We have all heard the analogy: Data is the new oil because it functions like a commodity. It’s highly sought after, it can make “tycoons” wealthy, and a drop of it isn’t very valuable compared to pools and pools of it.However, data isn’t oil; it’s not a stagnant resource pool waiting to be tapped into. Data is key to your business’s operations and driving the degree of growth or, if not governed correctly, speed of failure.
If data is anything like oil, it’s oil for your company’s machine that needs to be refined before it can be used.
If you have bad quality data, then you probably aren’t performing at your company’s potential and incurring high costs on an annual basis from missed opportunities, loss in productivity, damaged brand reputation and wasted resources.
So why overlook this vital element of the business and allow it to degrade? It’s much like your health. Daily preventative investments are going to be much more effective than retroactive attempts (with very high costs) to cure impairments from a lifetime of bad habits.
Why is Data Quality important?
Even after IBM projected a few years back that US businesses collectively are losing around $3.1 trillion dollars annually in costs related to bad data, many businesses still haven’t prioritized how to assess the current quality of their data. Yet, many companies still expect to implement some form of data-driven and/or AI strategy to improve business effectiveness.
Gartner estimates that 60% of B2B sales organizations will transition from relying on “experience to data-driven selling, merging their sales process, sales applications, sales data and sales analytics into a single operational practice.”
More recently, Gartner also published a new View from the Board of Directors 2021 survey in which 39% of the respondents stated that they want a digitally-driven transformation of their business model to be able to automate more of the sales and marketing operations. For these automations to be successful, complete and accurate data must be the bedrock for those processes.
GIGO is still relevant today
If we believe in George Fuechsel’s GIGO (garbage in, garbage out) concept, then companies are not going to be successful if they are feeding garbage into their models as only garbage will be outputted. It’s not that your models won’t produce results or predictions, but that the quality of those results will be inaccurate. To have these models and new machine learning strategies work, data needs to be improved and maintained proactively versus retroactively.
Let’s switch gears slightly and look into the aspects that influence the quality of data to be good or bad.
Key Dimensions of Data Quality
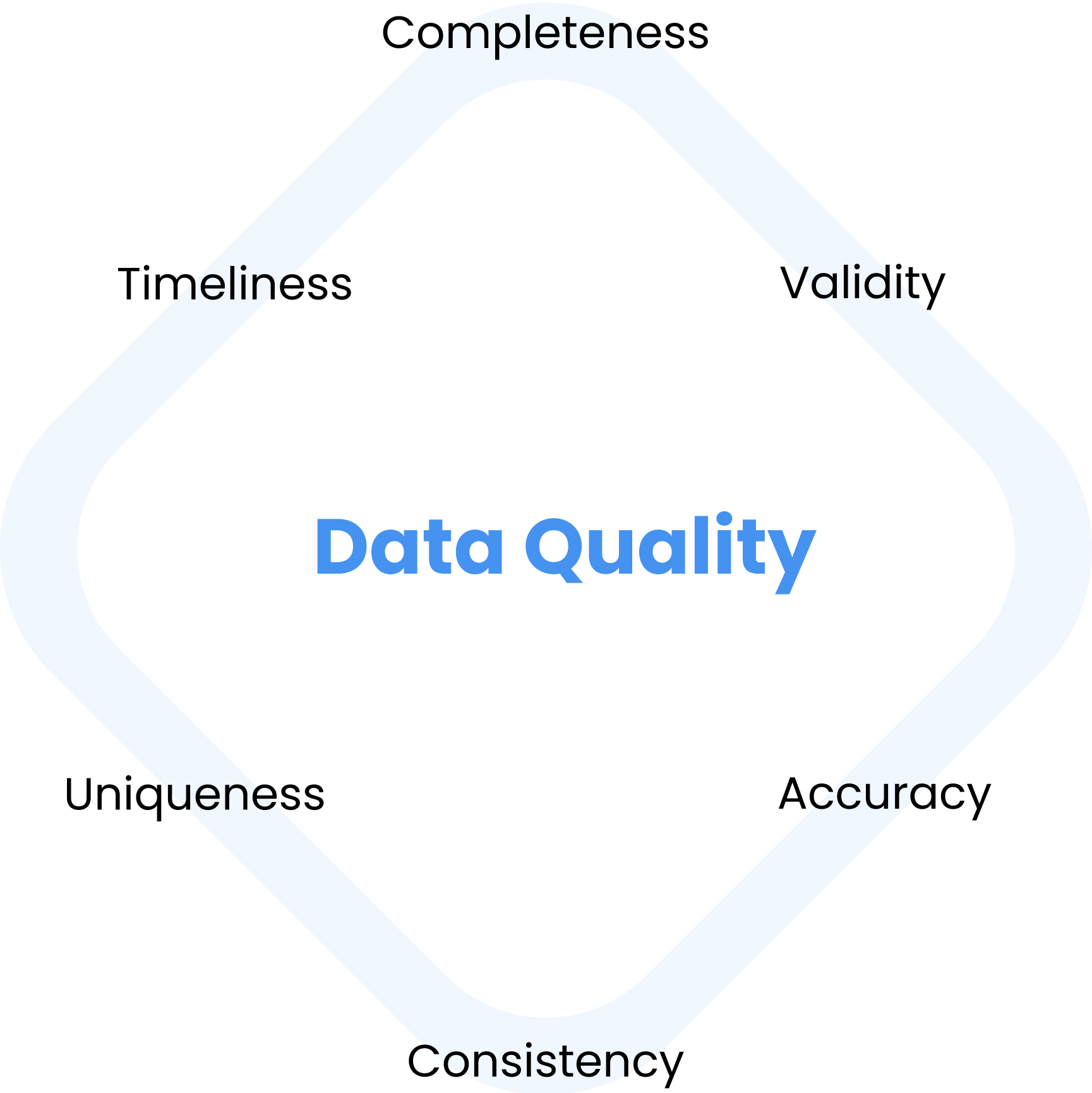
To correctly identify the best solution to improve the quality of your company’s data, one needs to understand the key characteristics of data. Data quality has many dimensions; let’s focus on six of the main ones: accuracy, completeness, consistency, timeliness, uniqueness and validity.
Completeness – Complete data refers to the existence of enough data inputed into the required fields and for the designated records. The best practice is to define the required fields for your business operations and then measure and monitor the completeness of the data inputted.
Validity – Validity is the degree to which data conform to a set of business rules, sometimes expressed as a standard or represented within a defined data domain. Validity is differentiated from both accuracy and correctness, each of which requires comparison to real-world objects to confirm.
Accuracy – This characteristic refers to whether or not the information is correct. Most often this dimension requires a 3rd party source of information to verify the correctness of the data. For example, are customer names and contact info the same as on their invoices or public profiles? Are websites still directing the users to the correct webpage?
Consistency – Data sources can be internal or external such as from a CRM/ERP or the web, but the key is that the variables and measurements used throughout the different sources are consistent with your data collection and usage processes.
Inconsistent data can lead to bad or misinformed decisions as the databases may be lacking certain information that exists in certain databases, but are not synchronized throughout the organization.
Uniqueness – Duplicate data is the bane of a successful customer journey. If duplicates aren’t driving your sales team crazy or causing distrust with the data, then they are preventing your support team from providing excellent service.
Duplicates can easily arise, but some of the causes can come from poor integrations, legacy data, lack of protocol across departments and human error.
Timeliness – Data needs to be up-to-date and timely. Research has been conducted on the rates of data decay and estimates that data in CRM databases can become suffer from rates as high as 2% monthly or about 30% annually.
Biznology even claims that the monthly rate is around 5%, which means 70% of data in B2B databases decays annually. These rates are driven by the changes that frequently occur in our lives such as changes in title or job function, name, address, email, phone number, etc.
Cost of Poor Data Quality
Bad data affects the entire business from marketing to sales and customer success in the form of:
- increased financial costs
- poor pipeline accuracy
- inaccurate forecasts
- missed opportunities
- damaged brand reputation
I’m not referring to bad data produced from machines such as the faulty data from malfunctioning sensors that can cause Boeing 737 crashes, but the data from human-involved processes.
Let’s face it, we are all fallible and this is true when we are working in our databases. Sometimes we accidentally delete some numbers or letters, enter information incorrectly, fail to update contacts, etc.
Bad quality of data can have severe impacts on the health of a business. Let’s take a deeper dive into the specific impacts:
1. Financial costs of bad data
Bad Decisions
Business leaders need good data in order to make good decisions (think GIGO). When marketing and sales teams have inaccurate information or outdated data in their databases, they are unable to make efficient decisions and ultimately waste resources.
For example, Forrester conducted a research on how bad quality data affects marketing teams and their findings suggest that 21 cents of every media dollar spent was wasted due to poor data (about $16.5 million average annual loss for enterprises).
Additional cost estimates:
- Gartner calculated annual financial costs at around $15 million on average.
- Ovum research estimates companies lose approximately 30% of revenue on average due to low data quality.
- MIT and other research consultants suggest the cost of bad data can range from 15% to 25% of revenue.
Productivity Loss
The result of bad decisions are mistakes and more mistakes require more time fixing. It becomes a very tedious and painful process for the organization when people are unable to trust the data and have to spend resources to fix incorrect data.
All teams suffer productivity losses when an organization has poor quality data. 32% of marketing teams’ time is spent on managing data quality and 26% of campaigns on average suffered from poor quality data.
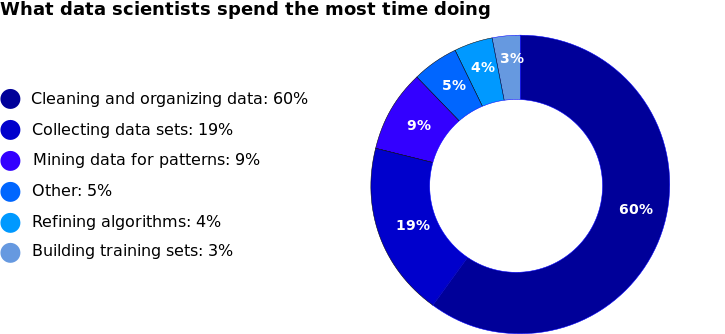
Research has estimated that data scientists can spend up to 80% of their time on the mundane tasks of collecting and preparing data before it can be refined into new value for the company.
2. How bad data causes missed opportunities
Poor quality data in your CRM can mislead your marketing and sales teams’ approach to landing and converting opportunities into successful deals. Bad proposals may be created and delivered as a result of poor data that served as the foundations for each one or it may be that potential opportunities are overlooked entirely.
Accurate and relevant opportunities will be more often secured when there is high-quality data fueling the identification, nurturing and conversion processes.
3. Why brands are negatively impacted by bad data
When data is incorrectly assessed as accurate, teams can make decisions that have negative consequences such as bad customer support and compliance issues.
Sending products to the wrong address or having one customer’s buying and support records split across duplicate contacts can create bad touch points with the brand.
Experiences are everything when it comes to customer relations and one bad experience, such as one bad interaction with a service agent, can cause the customer to switch brands.
When customers have to correct service teams about their account information or purchase history, this is not a positive experience. These bad touch points can lead to a bad customer experience and damage the brand’s reputation.
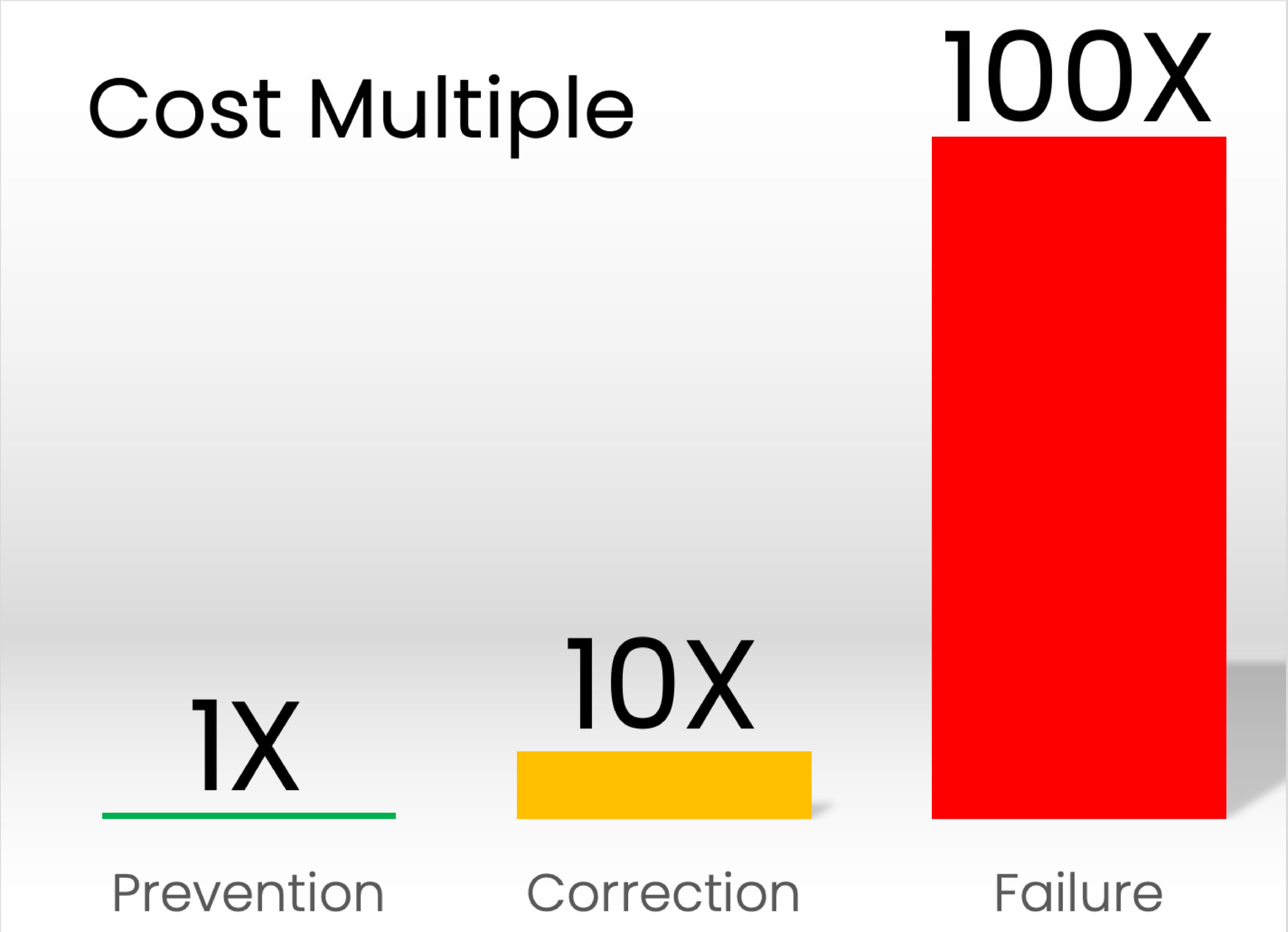
How Urgent is the Problem?
The answer can be found in the 1-10-100 rule. Fixing data quality retroactively is going to cost the business 10X more and potentially 100X more depending on the severity of the situation compared to investing in prevention methods.
The golden ticket that will protect higher profit margins for businesses is to begin proactively improving data quality.
It is estimated that every month 2% of companies’ CRM data becomes obsolete. Ignoring the quality of a company’s database can lead to CRM failure in just a few short years. This is why data quality has been identified as the No.1 cause of CRM failure.
Instead of waiting until the functionality of your CRM is tiptoeing around the precipice of failure and throwing one-time savior funds to pull it back from the edge, businesses should implement processes that prevent databases from getting near the edge in the first place.
The key is to figure out how to build a firewall that ensures only good data is being entered, saved and proactively updated in the company’s database.
Edited by Rachel Burger
Want to learn more about Delpha?